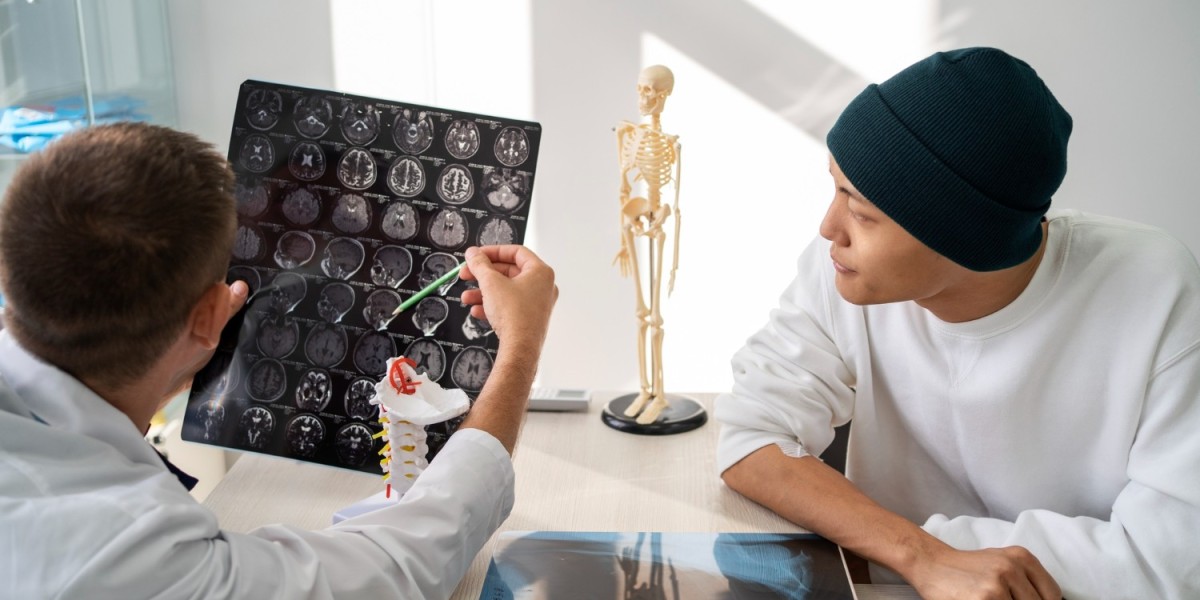
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers in the CNS, leading to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. The exact cause of MS is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications and self-care play a crucial role in managing MS. This may include regular exercise to maintain mobility and strength, adopting a healthy and balanced diet, managing stress levels, getting adequate rest and sleep, and seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and loved ones.
Living with MS can be challenging, both physically and emotionally, but with proper management and support, individuals with Multiple Sclerosis MS can lead fulfilling lives. Ongoing research and advancements in treatment options continue to provide hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for those affected by this complex neurological condition.
How common is multiple sclerosis (MS)?
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a relatively common neurological condition, although its prevalence varies geographically. It is estimated that approximately 2.8 million people worldwide have MS. The frequency of MS is higher in certain regions, particularly in North America and Europe, while it is relatively lower in Asia, Africa, and South America.
In the United States, it is estimated that around 1 million people live with MS. The condition often affects individuals between the ages of 20 and 50, and it is more common in women than men, with a female-to-male ratio of about 3:1.
The exact reasons for the geographic and demographic differences in MS prevalence are not yet fully understood. However, studies suggest that both genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of MS. Certain genetic variations have been identified as potential risk factors, but they do not fully account for the differences in prevalence. Environmental factors, such as vitamin D levels, exposure to sunlight, and certain infections, have also been investigated as potential contributors to the development of MS.
Overall, while MS is considered a relatively common neurological condition, its prevalence varies worldwide. Ongoing research is focused on further understanding the factors that influence the occurrence and distribution of MS, which can help in improving prevention strategies and developing targeted treatments.
What causes multiple sclerosis (MS)?
The exact cause of multiple sclerosis (MS) is not yet fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. MS is considered an autoimmune disease, meaning that the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In the case of MS, the immune system targets the protective covering of nerve fibers in the central nervous system (CNS).
There are several factors that are thought to contribute to the development of MS:
Genetics: MS has been found to have a genetic component, meaning that certain genes may increase the risk of developing the condition. However, having these genetic risk factors does not necessarily mean that an individual will develop MS. It is believed that a combination of genetic variations is involved, and more research is needed to fully understand their role.
Environmental Factors: Environmental factors are thought to play a significant role in triggering MS in individuals with a genetic predisposition. Some potential environmental factors include exposure to certain infections, such as the Epstein-Barr virus, which causes mononucleosis, as well as other viral or bacterial infections. Additionally, low levels of vitamin D, especially during early life, have been associated with an increased risk of developing MS.
Immune System Dysfunction: MS is considered an immune-mediated disease, suggesting that abnormalities in the immune system contribute to its development. It is thought that immune cells, particularly T cells, become activated and mistakenly attack the myelin, the protective covering of nerve fibers in the CNS. This immune response leads to inflammation, damage to the myelin, and disruption of nerve signals.
What are the symptoms of multiple sclerosis?
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) can present a wide range of symptoms that can vary greatly from person to person. The symptoms experienced depend on the location and extent of the damage to the central nervous system (CNS). Common symptoms of MS include:
1. Fatigue: Feelings of extreme tiredness and lack of energy are often reported by individuals with MS.
2. Numbness or Tingling: Many people with MS experience numbness or a sensation of pins and needles in different parts of their body, such as the arms, legs, face, or torso.
3. Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles, which can affect mobility and coordination, is a common symptom. This can result in difficulty walking, clumsiness, or difficulty with fine motor skills.
4. Balance and Coordination Problems: MS can cause issues with balance and coordination, leading to unsteady movements, stumbling, and difficulty with tasks that require precise movements.
5. Spasticity: Spasticity refers to muscle stiffness and involuntary muscle contractions, which can cause stiffness, pain, and difficulties with movement.
6. Vision Problems: Visual disturbances are common in MS. This can include blurred or double vision, loss of vision in one eye, or pain associated with eye movement.
7. Cognitive Changes: MS can affect cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities. Some individuals may experience difficulties with information processing or finding the right words.
8. Emotional Changes: MS can impact mood and emotions, leading to symptoms such as depression, anxiety, irritability, or emotional instability.
9. Bladder and Bowel Problems: MS can affect bladder and bowel function, leading to issues such as frequent urination, urgency, hesitancy, or constipation.
10. Sexual Dysfunction: Some individuals with MS may experience changes in sexual desire or function.
It's important to note that these symptoms can vary in severity and may come and go, depending on the type of MS and individual factors. Additionally, not everyone with MS will experience all of these symptoms. If you or someone you know is experiencing any concerning symptoms, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
What are the complications of multiple sclerosis?
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) can lead to various complications that can affect different aspects of a person's life. These complications can arise due to the progressive nature of the disease or as a result of specific symptoms and their impact on daily functioning. Some common complications of MS include:
1. Mobility Issues: As MS can affect muscle strength, coordination, and balance, individuals may experience difficulties with walking and overall mobility. This can lead to an increased risk of falls and injuries.
2. Fatigue: Fatigue is a common symptom in MS, and it can significantly impact a person's daily activities and quality of life. It may result in reduced stamina, decreased productivity, and increased difficulties in managing daily tasks.
3. Spasticity and Muscle Stiffness: Spasticity, characterized by muscle stiffness and involuntary contractions, can lead to discomfort, pain, and difficulty with movement and coordination.
4. Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction: MS can affect the nerves that control bowel and bladder function, leading to issues such as urinary urgency, frequency, or incontinence, as well as constipation or bowel incontinence.
5. Cognitive Changes: Some individuals with MS may experience cognitive changes, including difficulties with memory, attention, information processing, and problem-solving. These changes can affect daily activities and work performance.
6. Emotional and Psychological Impact: MS can have a significant impact on mental health, leading to increased rates of depression, anxiety, and mood swings. Coping with the uncertainties and challenges of the condition can also result in emotional stress and adjustment difficulties.
7. Sexual Dysfunction: MS can affect sexual function, leading to difficulties with libido, arousal, and orgasm. These changes can impact intimate relationships and quality of life.
8. Pain: Some individuals with MS may experience pain, including neuropathic pain, muscle pain, or headaches. This can range from mild discomfort to severe and chronic pain.
9. Secondary Health Conditions: MS can increase the risk of developing secondary health conditions such as osteoporosis, respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and infections due to immobility or compromised immune function