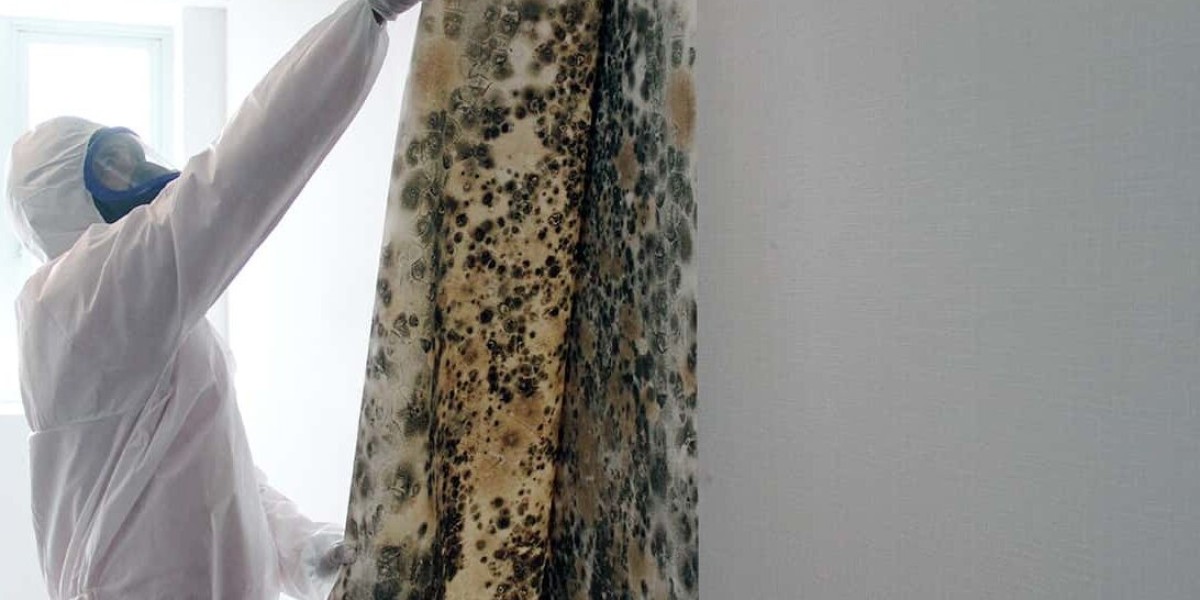
Mold growth is a pervasive issue that can impact the health of occupants and the structural integrity of buildings. Traditional mold removal methods often involve manual cleaning and chemical treatments, which can be time-consuming and may not effectively reach hidden mold colonies or airborne spores. In recent years, a cutting-edge solution has gained popularity in the field of mold remediation: mold fogging. In this article, we will delve into the concept of mold fogging, how it works, its advantages, and when it's a suitable option for addressing mold problems.
Understanding Mold Fogging
Mold fogging, also known as fogging for mold remediation, is a specialized technique that employs a fogging machine to disperse a mold-fighting solution in a fine mist or fog throughout the affected area. This mist reaches virtually every surface and crevice, including hidden mold growth, and can effectively neutralize mold spores and inhibit further growth.
How Mold Fogging Works
Mold fogging typically involves a series of steps:
Assessment: Begin by assessing the extent and location of the mold infestation. It's crucial to identify the type of mold, the affected areas, and any potential sources of moisture.
Containment: To prevent the spread of mold spores during the fogging process, the affected area is often sealed off using plastic sheeting and tape. HVAC systems may also be turned off to avoid distributing mold spores throughout the building.
Preparation: Mix the mold-fighting solution according to the manufacturer's instructions. The solution may vary depending on the severity and type of mold infestation.
Fogging: Activate the mold fogging machine, which transforms the liquid mold-fighting solution into a fog. This fog is released into the sealed area, saturating the air and surfaces.
Dwell Time: Allow the fog to settle and the mold-fighting solution to come into contact with mold spores and growth. The dwell time can vary based on the product used.
Ventilation: After the recommended dwell time, ventilate the area thoroughly to disperse any remaining fog and airborne particles. This is typically achieved by opening windows and using fans.
Advantages of Mold Fogging
Comprehensive Coverage: Mold fogging ensures that the mold-fighting solution reaches all surfaces, including hidden areas that are difficult to access manually.
Efficiency: Fogging is a relatively quick process, reducing the time and effort required for mold remediation compared to traditional cleaning methods.
Uniform Application: Fogging provides consistent and uniform coverage, reducing the chances of missing mold-prone spots.
Preventive Measure: Mold fogging can also serve as a preventive measure in high-humidity environments or after water damage to inhibit future mold infestations.
When to Consider Mold Fogging
mold fogging can be a suitable solution in various scenarios, including:
Extensive Mold Infestations: When mold growth is widespread, deeply rooted, or in hard-to-reach areas.
Airborne Mold Spores: To address airborne mold spores that may not be effectively removed by surface cleaning alone.
Preventive Maintenance: As part of regular maintenance in areas prone to mold growth or after incidents of water damage to prevent future mold issues.
Conclusion
Mold fogging is a revolutionary approach to mold remediation that offers comprehensive coverage, efficiency, and consistency. It has gained popularity as a powerful tool in addressing mold problems, especially in cases of extensive infestations or where traditional methods may fall short. However, it's essential to follow safety guidelines, use appropriate solutions, and consider seeking professional assistance for severe mold issues. By embracing mold fogging as a part of mold remediation efforts, property owners and managers can maintain a safe and mold-free indoor environment, protecting both the well-being of occupants and the integrity of the building structure.