Market Overview
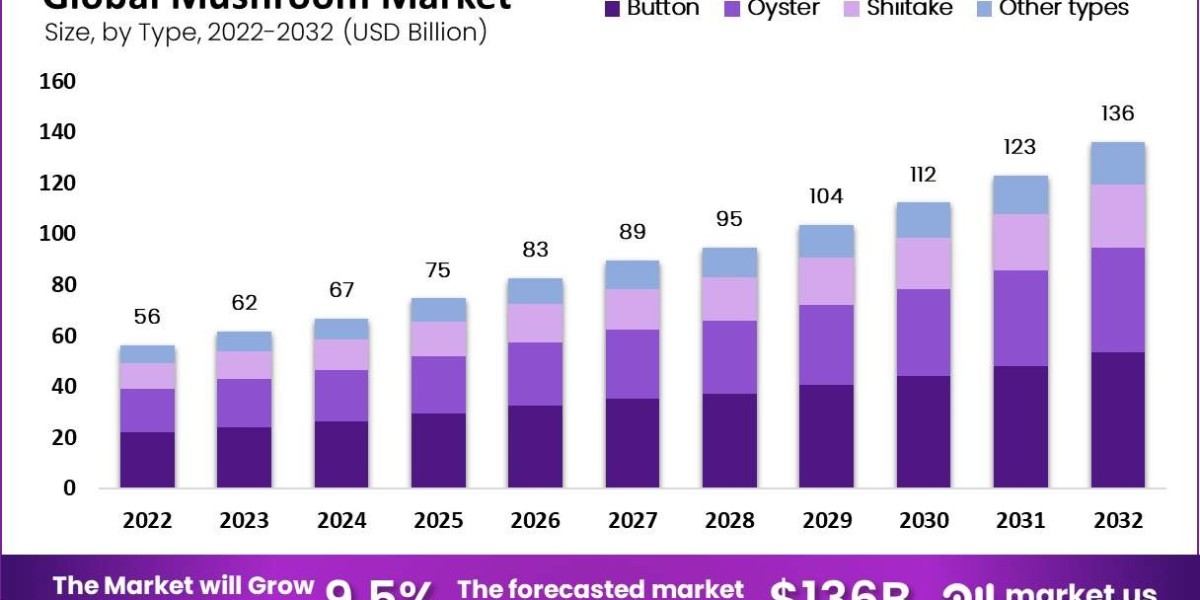
The global Mushroom Market was valued at USD 56 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.5 % from 2023 to 2032, reaching USD 136 billion by 2032.
The global mushroom market has experienced significant growth and is expected to continue expanding in the coming years. Mushrooms are widely consumed worldwide due to their nutritional value, versatility in culinary applications, and potential health benefits. The market encompasses various types of mushrooms, including button mushrooms, shiitake mushrooms, oyster mushrooms, and others
Top Key Players
· Drinkwater Mushrooms
· Bonduelle Group
· CMP Mushroom
· Menterey Mushroom, Inc
· Greenyard
· The Mushroom Company
· Monaghan Group
· Shanghai Fengke Biological Technology Co., Ltd
· OKECHAMP S.A
· Other Key Players
Get a free Sample Copy of This Report https://market.us/report/mushroom-market/request-sample/
Key Market Segments
By Type
· Button
· Shiitake
· Oyster
· Other types
By Form
· Fresh
· Processed
By Distribution Channel
· Supermarkets & Hypermarkets
· Convenience Stores
· Specialty Stores
· Online Stores
By End-user
· Food
· Pharmaceutical
Demand and Trends:
- Increasing Consumer Awareness and Health Consciousness: Consumers are becoming more aware of the nutritional benefits and potential health advantages of mushrooms. Mushrooms are low in calories, fat-free, and rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They are also known for their potential immune-boosting and anti-inflammatory properties. As consumers prioritize healthier food choices, the demand for mushrooms as a nutritious ingredient has grown.
- Rising Popularity of Plant-Based Diets: The growing adoption of plant-based diets, including vegetarian and vegan lifestyles, has significantly contributed to the demand for mushrooms. Mushrooms are often used as a meat substitute or complement due to their meaty texture and umami flavor. They provide a source of plant-based protein and can be incorporated into various dishes, such as burgers, stir-fries, and pasta sauces.
- Culinary Versatility and Ethnic Cuisine Influence: Mushrooms are highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of culinary applications. They are popular in various cuisines worldwide, including Asian, European, and North American cuisines. The culinary versatility of mushrooms, along with the influence of ethnic cuisines, has driven the demand for different mushroom varieties and expanded their usage in diverse recipes.
- Growing Demand for Specialty and Exotic Mushrooms: There is an increasing demand for specialty and exotic mushrooms, such as shiitake, oyster, enoki, and lion's mane mushrooms. These varieties offer unique flavors, textures, and nutritional profiles, appealing to consumers seeking novel culinary experiences. The demand for specialty mushrooms has led to their wider availability in supermarkets and specialty stores.
- Functional and Medicinal Mushroom Products: Mushrooms with specific health benefits, such as reishi, Chaga, and cordyceps, have gained popularity as functional and medicinal mushrooms. These mushrooms are often consumed in the form of supplements, extracts, or powders, as they are believed to have immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory, and adaptogenic properties. The demand for functional and medicinal mushroom products has increased as consumers seek natural alternatives for health and wellness.
- Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly Image: Mushrooms are considered a sustainable and environmentally friendly crop. They can be grown using agricultural waste or byproducts, reducing waste and promoting circular economy practices. The sustainable and eco-friendly image of mushrooms has resonated with environmentally conscious consumers, contributing to their demand.
Technological Innovations:
- Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA): Controlled environment agriculture, including indoor farming and hydroponics, has revolutionized mushroom cultivation. These technologies allow for precise control of temperature, humidity, light, and other environmental factors, creating optimal conditions for mushroom growth. CEA enables year-round production, reduces dependence on seasonal availability, and increases overall crop yields.
- Automated Cultivation Systems: Automation has been introduced in various stages of mushroom cultivation, from substrate preparation to harvesting. Automated systems help streamline processes, reduce labor requirements, and improve efficiency. For example, automated substrate mixing and filling machines ensure consistent substrate quality and reduce manual labor. Automated harvesting systems can accurately identify and harvest mature mushrooms, increasing productivity.
- Advanced Growing Substrates: Innovations in growing substrates have improved mushroom cultivation. Traditional substrates, such as composted agricultural waste, have been supplemented or replaced with alternative materials like straw, wood chips, and agricultural residues. These substrates offer better control over nutrient content, moisture retention, and disease prevention, resulting in improved mushroom yields and quality.
- Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering: Biotechnology and genetic engineering techniques have been employed to enhance mushroom traits. Researchers have developed genetically modified mushrooms with improved resistance to diseases, pests, and environmental stressors. These advancements help ensure higher crop yields, reduce losses, and enhance the overall sustainability of mushroom cultivation.
- Post-Harvest Technologies: Technologies for post-harvest handling and processing of mushrooms have also advanced. Innovations in packaging materials, such as modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), help extend the shelf life of mushrooms by controlling gas composition and moisture levels. Cold chain management technologies, including temperature-controlled storage and transportation, ensure the freshness and quality of mushrooms throughout the supply chain.
- Value-Added Mushroom Products: Technological innovations have led to the development of value-added mushroom products. For example, mushroom extracts, powders, and concentrates are produced using advanced extraction techniques to concentrate the bioactive compounds present in mushrooms. These products are used in the food, beverage, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical industries, offering convenient and versatile ways to incorporate mushroom benefits into various applications.
Supply chain analysis:
- Production: The first stage of the supply chain is mushroom production. Mushrooms are cultivated in specialized farms or facilities. The production process involves selecting the right mushroom variety, preparing the growing medium, inoculating the medium with mushroom spawn, and providing the necessary environmental conditions for growth, such as temperature, humidity, and light.
- Processing: Once the mushrooms are harvested, they undergo processing to enhance their shelf life and prepare them for distribution. Processing may involve cleaning, sorting, grading, and packaging the mushrooms. Some mushrooms may also be processed into value-added products like dried mushrooms, mushroom powders, or mushroom extracts.
- Distribution: After processing, the mushrooms are transported to distribution centers or wholesalers. Distribution channels may vary depending on the market and region. Mushrooms are typically transported in refrigerated trucks or containers to maintain their freshness and quality during transit.
- Retail: From the distribution centers, mushrooms are supplied to various retail outlets, including supermarkets, grocery stores, restaurants, and farmers' markets. Retailers play a crucial role in ensuring that mushrooms reach the end consumers. They may also handle further processing, such as slicing or packaging mushrooms for consumer convenience.
- Consumer: The final stage of the supply chain is the consumer. Consumers purchase mushrooms from retail outlets for personal consumption or use in food preparation. The demand for mushrooms is influenced by factors such as consumer preferences, health benefits, culinary trends, and availability.
Contact us:
Global Business Development Team: Market.us
Market.us (Powered By Prudour Pvt. Ltd.)
Send Email: inquiry@market.us
Address: 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300 New York City, NY 10170, United States
Tel: +1 718 618 4351, +91 78878 22626