Homesteaders must learn how to extend the growing season in their Hardiness Zone to sell crops to supplement their income. It will be challenging to generate the majority of your revenue from your garden if the cultivation period is only twenty weeks long. Gardening for profit would be much easier if you could extend your growing season by at least ten weeks. Fortunately, you can do it by using a high tunnel.
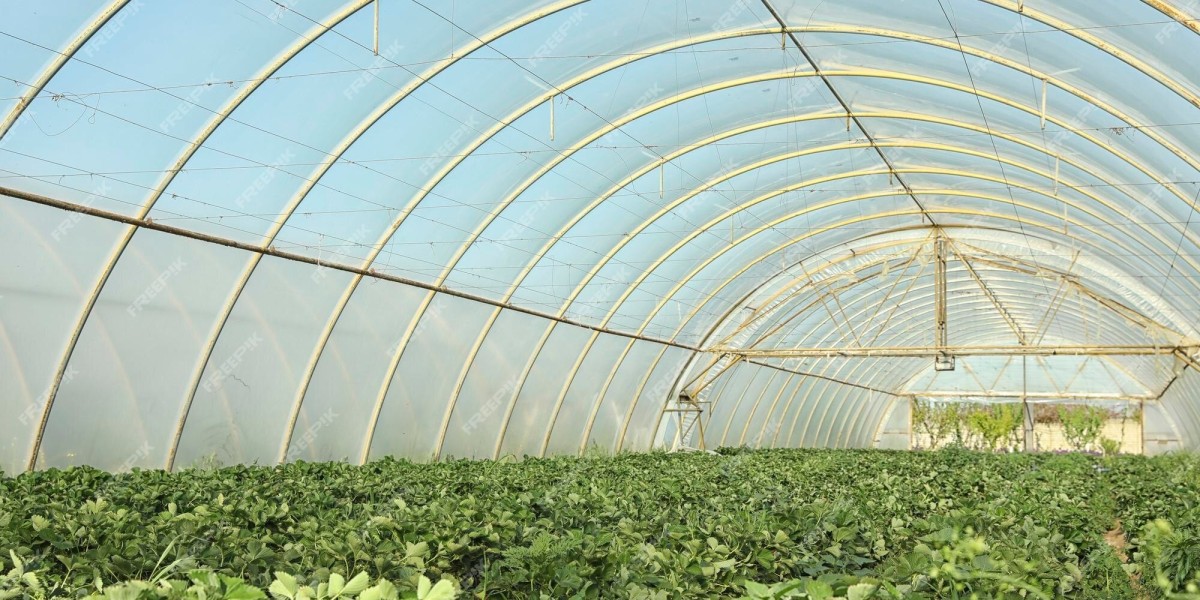
A high tunnel, often called a hoop house or hoop tunnel, is a partially permanent building that lengthens the growing season and enables planting to start at least four weeks sooner in the spring and extend six weeks later in the fall. If you use plastic to cover your soil, you can begin planting even sooner. On a sunny day, the interior of a high tunnel is 30 to 50 degrees warmer than the surrounding air. The temperature causes an acceleration in the germination of seeds and plant development. Additionally, it enables you to farm year-round by allowing you to gather cold-hardy vegetables.
Low-tunnel hoop houses, high-tunnel hoop houses, full-tunnel hoop homes, and greenhouses are the three most prevalent forms of hoop homes or hoop houses. Hoop homes come in many modifications from these basic types, each tailored to a particular aspect of a grow operation or crop. Suppose you are confused as to what hoop house to buy. In that case, you must consult with a commercial hoop house kits manufacturer who can provide the right guidelines, explain features and functionality, and how to improve cultivation in your homesteading.
Many different high tunnel designs exist, but a tall-sided tunnel will give you more workspace and adequate ventilation. If you reside in a region with a lot of snow, choose a tunnel with a peak to prevent collapse during a significant snowfall. Choose a high tunnel with readily rollable walls to prevent your plants from scorching and steaming on hot days. If your area experiences extreme cold for extended periods, consider introducing portable, small heaters that can be easily turned on amid the coldest weather.
How you will supply water to your plants is one of the most important considerations when picking a house hoop. Since there won't be any rain, you must choose a system for irrigation. Any rain that pours on the hoop house should ideally be collected and used to irrigate the plants.
Most kits don't include it because research on effectively accomplishing this is ongoing. The system that is advised for use is drip irrigation, which offers several advantages. First, there is very little water waste because the water is sent straight to the root zone. Second, a drip irrigation system lowers the danger of some fungal diseases and crop water damage since it provides water directly to the roots. Finally, a drip system enables you to directly inject fertilizer into the system to provide fertilizer to your crops as needed.
Although planting in a hoop house has the most obvious benefit of extending the growing season, other advantages exist. Hoop houses protect against extreme weather, including ferocious winds, torrential rain, snow, and drought. They aid in shielding young, defenceless plants from scorching and sunburn.
Hoop houses are used to prevent weeds, diseases, and pests. Row covers and bug screens can be installed along the sidewalls and apertures to provide further pest protection. The greatest method of disease prevention is always proper hygiene paired with other smart gardening practices like monitoring the crops and crop rotation. By putting down a thick covering of straw among rows and around certain plants, weeds can be controlled.
Tomatoes, melons, eggplant, lettuce, cucumbers, broccoli, salad greens, herbs, bell peppers, turnips, spinach, radishes, summer squash, and other common plants and crops include these.
Greenhouses versus Hoop Houses
What distinctions exist between a hoop house and a greenhouse?
Yes. Hoop houses and greenhouses are all significantly different: they are built in the field directly over the growing area. They are typically constructed with steel tubes, a little hardware, and one or two layers of plastic or greenhouse fabric. Most of the time, however, commercial and industrial greenhouses are entirely enclosed and built on a concrete slab, enabling perfect control of the environment over the entire grow operation.
Hoop houses offer many advantages to homesteaders who depend on their gardens for income. Due to a longer growing season, quicker development, and enhanced production, gardening in a hoop house results in a greater output and yield. Customers enjoy having access to farm-fresh products first, which keeps them returning. When a product is out of season, customers can get it from a local grower, but the cost will be higher.
Growing various fruits, vegetables, and flowers in hoop houses is productive all year. A hoop house is a terrific investment whether you wish to serve your loved ones food that you are happy about or sell your produce as a substantial source of income.