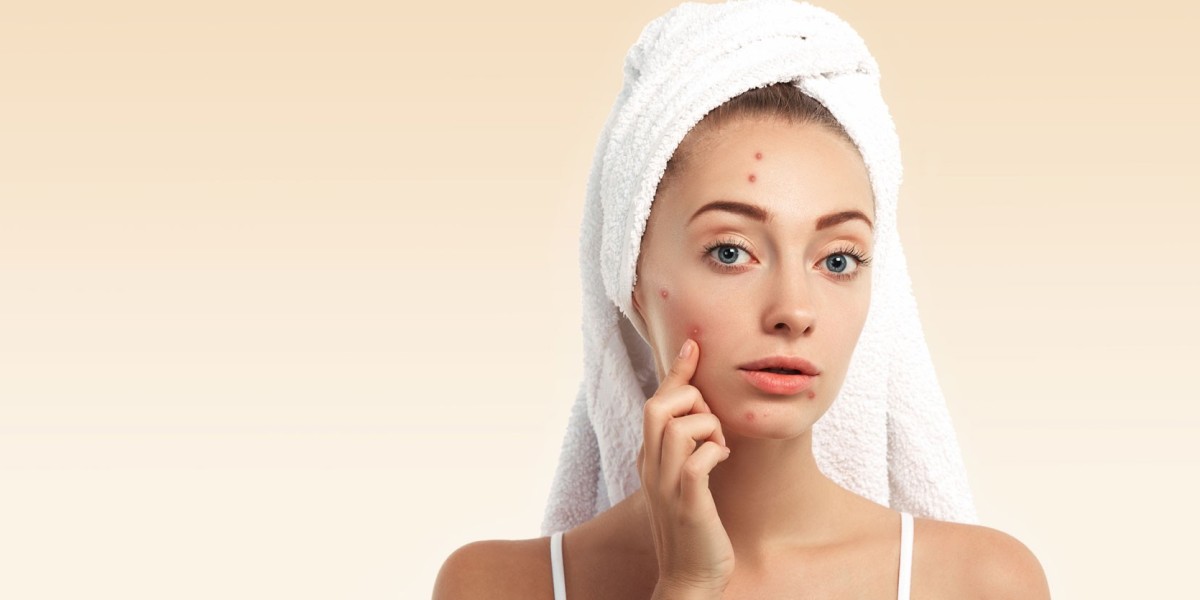
Acne is one of the most well-known skin problems globally. Acne is something that almost everyone has dealt with at some time in their life. It is caused by the blocking of skin pores with dead skin cells, excess sebum, debris, and occasionally acne-causing bacteria. Acne is most often found on the face in 99% of instances. It can also be found on the back (in 60% of instances) and the chest (15% of the time). Acne can appear on the neck, shoulders, and upper arms.

This post will discuss everything that one needs to know about acne. The information taken from Dr. Ravali Yalamanchili, who offers the best acne treatment in Hyderabad has helped us in making this blog insightful and helpful. So, let’s start by learning the causes of acne.
What Causes Acne?

Acne/pimples form when skin pores get blocked and the pilosebaceous glands (which include the sebaceous glands and hair follicles) become irritated. Two things come into play here: hormonal shifts and acne-causing bacteria.
- Hormones: Teenagers are more likely to develop acne because their androgen levels- the male sex hormones increase as they enter puberty. Sex hormones stimulate the body to create more sebum (natural skin oils) from the sebaceous glands.
- Bacteria that Cause Acne: Excess sebum clogs hair follicle openings, and bacteria feed on these oils. These bacteria thrive, causing inflammation. The follicular walls rupture due to the pressure of the sebum and bacteria buildup. When this happens, sebum oozes into the surrounding skin tissues, forming inflammatory acne papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts.
What are the Different Types of Acne Spots?
There are several varieties of acne. Some are anti-inflammatory, while others are pro-inflammatory. The following are examples of inflammatory types:
- These are pink, inflammatory lesions caused by excess oils, dead skin cells, and acne-causing bacteria clogging and rupturing hair follicles.
- These are more advanced papules that show little red pimples with a white top loaded with pus and oil.
- These are significantly bigger lesions that form beneath the skin, most often in the dermis (middle skin layer). They are hard, painful lumps that contain excess natural skin oil, dead skin cells, and infection transmitted beneath the skin from a burst hair follicle. Acne scars can form if they are scraped or irritated.
- These are also big skin lesions that form in the dermis of the skin. They are soft to the touch, bloated, uncomfortable, pus-filled, and can leave acne scars.
The Non-inflammatory Types Include:
- Open comedones feature a large aperture made up of dead skin cells and sebum plugs that allow air to readily pass through. When air comes into touch with hair follicles that are blocked with abundant sebum and dead skin cells, chemical reactions occur that cause the hair follicles to become black, hence the term "blackheads."
- Closed comedones have a small aperture through which air cannot enter the hair follicles, preventing the follicle from becoming black. As a result, certain forms of acne patches remain white, and they are frequently referred to as whiteheads.
- Acne vulgaris is the most prevalent kind of acne. This form of acne is classified as mild, moderate, or severe and is most common in teens. Dermatologists and other healthcare practitioners use these categories to diagnose acne. However, there are additional, lesser-known kinds of acne, such as acne rosacea, cosmetic acne, and smoker's acne, which differ in their causes.
What Are Treatments For Acne?

Acne treatments vary depending on the patient's age or gender, as well as the severity of the acne. Topical creams or gels can be used to treat mild to severe acne. Hormone-controlling medicines and oral antibiotics can be useful for more inflammatory acne types. There are a variety of medications available to treat obstinate or severe acne. Additionally, dermatologists use a variety of alternative acne treatment techniques. The finest acne treatment inhibits bacterial development, limits sebum production, promotes skin cell shedding to clear pores, and lowers testosterone levels in the body. These are some examples:
Topical Treatments
- Vitamin A retinol derivatives aid in the unclogging of pores and the prevention of new acne lesions.
- Benzoyl Peroxide destroys microorganisms on the skin, soothes irritation, and aids in the unclogging of pores.
- To minimize germs and inflammation, antibiotics such as clindamycin or erythromycin can be administered to the skin.
- Salicylic acid aids in the unclogging of pores and the exfoliation of dead skin cells.
Oral Medications
- Antibiotics. To minimize inflammation and bacteria, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline might be administered.
- Female oral contraceptives and birth control tablets can be beneficial in balancing hormones and decreasing acne.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane) is used only in severe situations. It is a potent drug that decreases oil production and has long-term effects. It has the potential for adverse effects and must be carefully monitored.
Carbon Laser Peel

The dermatologist applies a thin coating of activated carbon to the affected region in this treatment. As the liquid carbon dries, it penetrates deep into the skin. The laser light is then directed at the therapy spot. The laser light is absorbed by the carbon particles and thermally destroyed, along with the skin detritus that has blocked the pores. This acne treatment is good for oily skin, deep pores, blackheads, whiteheads, and inflammatory acne.
Laser Treatment
Acne light therapy and laser treatment are particularly successful in removing facial marks. The laser's heat kills or inhibits the development of acne-causing bacteria while also reducing sebum production. Multiple treatment sessions are necessary to achieve benefits that are considerably better than a single session.
Note: It is important to remember that what treatment should be used and what treatment will suit one best can only be determined by a skilled dermatologist. To do so, the skin specialist will perform a thorough analysis of the acne to identify the type of acne. This way it would help provide effective treatment.

For more information about acne treatment, one can get a consultation with Dr. Ravali Yalamanchili, the best Skin Specialist in Hyderabad. To do so, visit Neya Dermatology & Aesthetics Clinic now.
Original Source:- https://www.articleshore.com/acne-its-causes-effective-treatments/