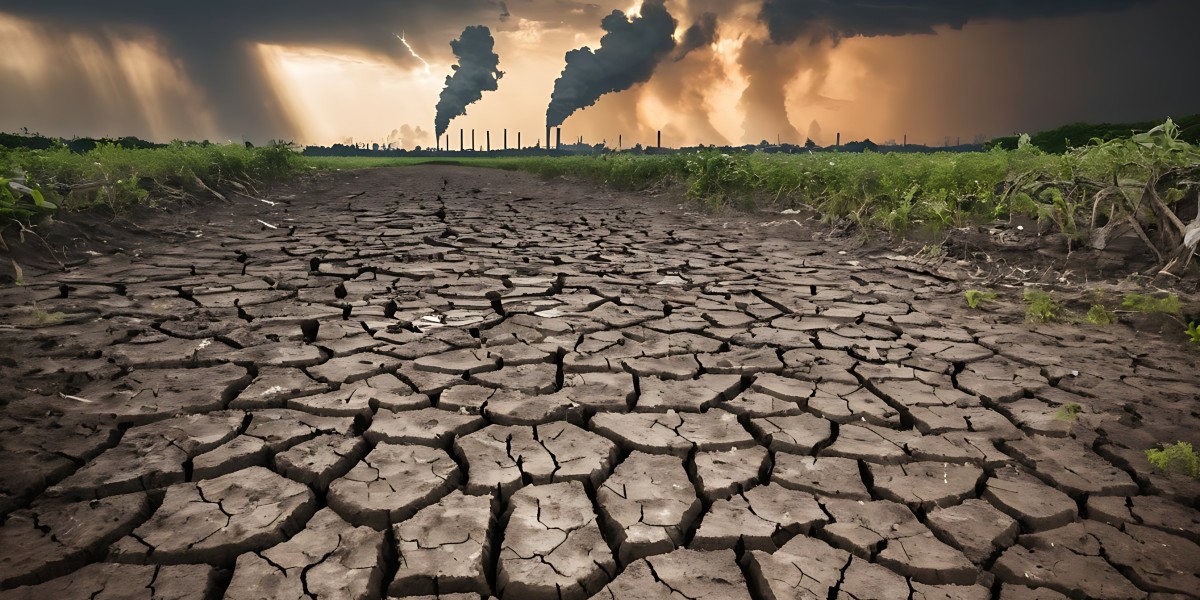
The Earth is undergoing a profound transformation, with the climate evolving at an unprecedented pace over the past five decades. The impact of human activities on the environment has led to a series of alarming changes, reshaping the planet as we know it. In this blog post, we will delve into the key shifts in climate patterns observed over the last 50 years and the implications for our planet's future.
Historical Overview
The journey through the last half-century begins with a look at the baseline climate conditions in the early 1970s. Back then, global temperatures were relatively stable, and weather patterns followed familiar cycles. However, as industrialization accelerated and greenhouse gas emissions soared, the delicate balance of the Earth's climate began to unravel.
Rising Temperatures
One of the most striking trends is the consistent rise in global temperatures. According to data from world-weather.com.de, the average global temperature has increased by approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius since 1970. This seemingly small shift has profound implications, triggering a cascade of effects on ecosystems, weather patterns, and sea levels.
Extreme Weather Events
The frequency and intensity of extreme weather events have become more pronounced over the past five decades. Hurricanes, typhoons, droughts, floods, and wildfires are now occurring with greater regularity and ferocity. These events not only pose immediate threats to human safety and infrastructure but also have long-term consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Melting Ice Caps and Rising Sea Levels
Perhaps one of the most visually striking changes is the rapid melting of polar ice caps and the subsequent rise in sea levels. Satellite imagery and scientific studies show that the Arctic and Antarctic regions have lost a significant amount of ice, contributing to the swelling of oceans worldwide. This phenomenon poses a direct threat to coastal communities and low-lying areas, emphasizing the urgency of addressing climate change.
Ocean Acidification
The oceans, acting as a critical carbon sink, have absorbed a substantial amount of carbon dioxide emitted by human activities. However, this has led to a concerning side effect – ocean acidification. As the acidity of seawater increases, marine life, especially organisms with calcium carbonate skeletons, face unprecedented challenges, potentially disrupting entire marine ecosystems.
Impact on Biodiversity
The changing climate has triggered shifts in ecosystems, affecting the distribution and behavior of plant and animal species. Some species are struggling to adapt, leading to population declines and, in some cases, extinction. The interconnected web of life on Earth is facing unprecedented disruptions, and urgent action is needed to mitigate these impacts.
Human Health and Social Implications
Beyond environmental concerns, the changing climate has direct implications for human health and social well-being. Increased heatwaves, changes in disease patterns, and the potential displacement of communities due to sea-level rise are all factors that demand attention and proactive solutions.
Global Efforts and Policy Initiatives
Recognizing the severity of the climate crisis, the international community has come together to implement various initiatives and agreements aimed at mitigating climate change. The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, stands as a landmark effort to limit global temperature increases and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, the effectiveness of these measures depends on global cooperation and sustained efforts by all nations.
Conclusion
As we reflect on the past 50 years, it is evident that the Earth's climate has undergone unprecedented changes, largely driven by human activities. The urgency to address climate change has never been greater, and collective action is paramount. By understanding the historical context and acknowledging the scientific evidence, we can work towards sustainable solutions that preserve the planet for future generations.